IOTA Joins Project Funded by Japanese National R&D agency NEDO to Build AI and DLT-based Predictive Maintenance System
We’re proud to announce that the IOTA Foundation has partnered on a project initiated by Best Materia and IMC, Japanese maintenance-related companies, and funded by NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization). NEDO is Japan’s largest public management organization promoting research and development as well as the deployment of industrial, energy, and environmental technologies. The goal of the project is to develop technology to strengthen the security, longevity, and durability of critical infrastructure assets in Japan and abroad.
By adding artificial intelligence and the IOTA Tangle technology to Risk-Based Maintenance (RBM) Systems deployed in power plants, energy plants, industrial plants, petrochemicals, and oil refining plants, the group hopes to capture a large share of the domestic social infrastructure conservation market, valued at 170 Trillion Yen (1.5 Trillion USD).
This type of predictive maintenance system that shares industry data using a distributed database is set to be the first of its kind in the world.
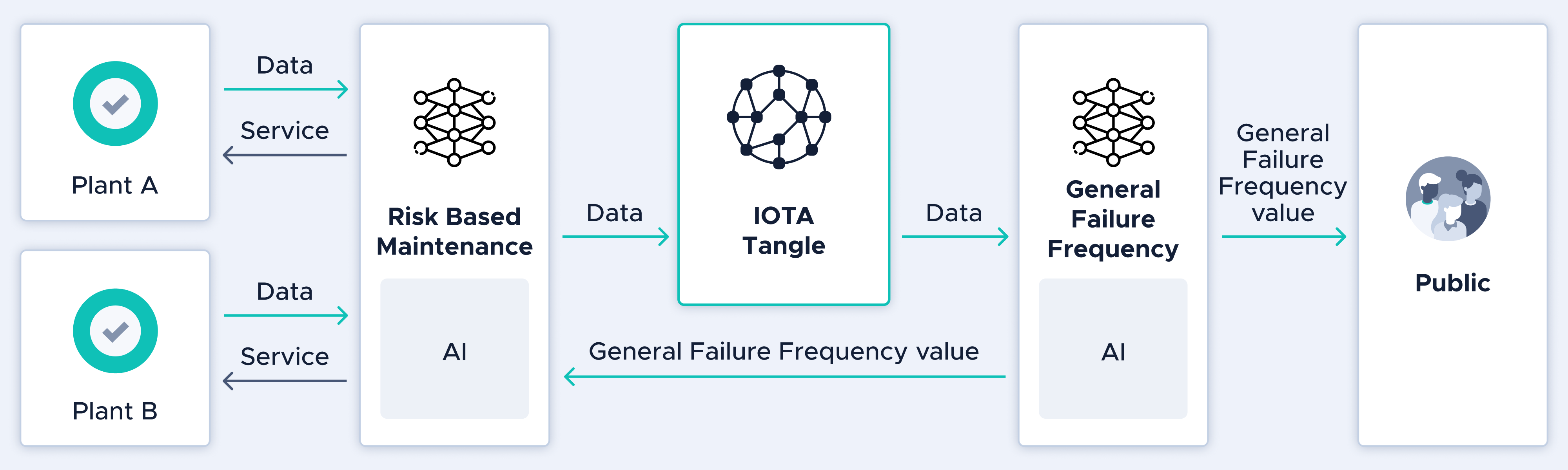
While damage prediction assessment based on the current RBM standards exists, most processes are still left up to field workers to do manually. To further optimize these systems, maintenance data will be digitized and processed by an artificial intelligence system to predict when and which parts in a plant are going to require maintenance. This will reduce unplanned outages, improve plant availability and lower costs by reducing unnecessary inspections and repairs.
“Creating a decentralized, open-source, and free distributed ledger technology to ensure data integrity has always been our driving purpose. As a non-profit, we are honored to see the IOTA protocol being utilized to secure a wide variety of data points in this project. Digitalizing the RBM systems for safer and more efficient industrial plants is only one of many applications where IOTA will be used in the future.” Holger Köther, Director of Partnerships, IOTA Foundation
“Because of the aging problem in Japan, we seriously need the AI system supporting our business in place of retired RBM consultants. We expect that IOTA tangle will enable us to securely collect and store RBM-related data including sensitive plant information which is the key to the accuracy of the AI system.” Shigemitsu Kihara, CEO, Best Materia
The project will develop a cloud-based SaaS software with the following capabilities:
●A decentralized database using IOTA’s distributed ledger technology-Centralized databases are vulnerable to accidents, tampering, and leakage. By building an RBM using IOTA, maintenance companies are able to provide a solution to infrastructure partners that is resistant to cyber-attacks while protecting sensitive data.
●Artificial intelligence system developed-With current RBM systems, individuals are dependent on the knowledge of skilled technicians making standardization difficult. Due to Japan’s aging population, there is a serious risk of information loss when current employees retire. By creating an artificial intelligence system, information can be captured, shared, and acted upon by distributed teams across the world.
●Digitizing and sharing infrastructure data-Right now, data for plants across Japan are stored manually and not digitized. This can cause a host of issues when it comes to the integrity and sharing capabilities of data. By digitizing infrastructure data, maintenance companies can make it easier for partners across the supply chain to collaborate and share data in a safe, efficient way.
Key Statistics About The Project:
● For Data digitization (supporting initial data input by skilled engineers from paper to PDF, PDF to RBM software), the labor cost of skilled engineers per plant is 20–30 million yen.
● Maintenance personnel cost of a distributed database and AI is 30 million yen/ year.
● There are 30,000 plants that require initial input for RBM system construction in Japan.
● The initial data input contract cost for one plant is 30–50 million yen, 0.9–1.5 trillion yen.
● The initial data input subcontracting cost for one plant is 30 to 50 million yen, and if AI is advanced in this research and development, the cost will be less than half.
In the future, this AI and IOTA enabled risk-based maintenance technology, that is pioneered in this project, will contribute to the creation of new industries. For example by combining 5G and IoT on-site sensors we can improve the current more manual approaches to gathering data. In addition to that, the same technology that will be used in plants can potentially be used in other industries like the manufacturing of goods and the construction of roads and bridges as well.
About NEDO
NEDO is an Independent Administrative Agency under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industries, Japan. In 2020, it allocates over 1.38 Billion dollars to domestic/international R&D projects by private companies and universities in Japan.
NEDO plays an important role in Japan’s economic and industrialization policies through its funding of technology development activities. NEDO also acts as an innovation accelerator to realize its two basic missions of addressing energy and global environmental problems and enhancing industrial technology. It does this by coordinating and integrating the capabilities of industry, academia, and government.
To read the PR in Japanese click here!
For more information about IOTA, visit: https://www.iota.org/
Follow us on our official channels and get the latest news!