An Introduction to the Business Ecosystem of IOTA
Understanding the Different Components and Engagements of IOTA
The IOTA Foundation builds open-source software to enable a new type of digital infrastructure that empowers people to live freely and securely in a digital world. To do this, the Foundation engages with many different initiatives, markets and partners in academia, government and businesses.
Because it can take some time to understand the dependencies of what we do, we have created an infographic that shows the different components of the IOTA ecosystem, and how they interact in the technical realm while keeping standardization and industry needs in mind.
You can open the infographic here and refer to it while reading through the article. With new functionalities being developed on top of the IOTA Tangle, we will update the graphic to reflect these new functionalities.
In this article, we will look at the different components from the bottom up. Let’s start with the node software.
Node Software
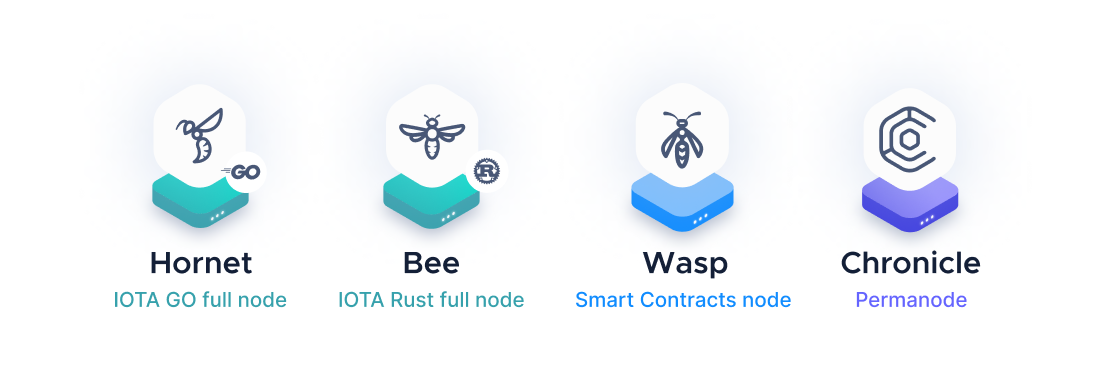
The Hornet and Bee node software manage the ledger state of IOTA and make up the IOTA network. The IOTA mainnet is public, but all components can be set up locally or in the cloud to install a private Tangle for academic or any other purposes. Chronicle is a permanode software to store and query a large number of transactions in a fast and efficient manner. The Wasp node will be the relevant node software for smart contract execution.
More information on the different nodes can be found in our recent blog post Incentives to run an IOTA Node
The Tangle
A network of nodes creates the distributed IOTA network, the Tangle. The Tangle provides the basic functionality and security of the IOTA protocol and defines its key characteristics. Once written to the Tangle, data cannot be deleted or changed. Due to the design of IOTA, it does not require miners to validate transactions. Instead, new transactions validate previously sent transactions.
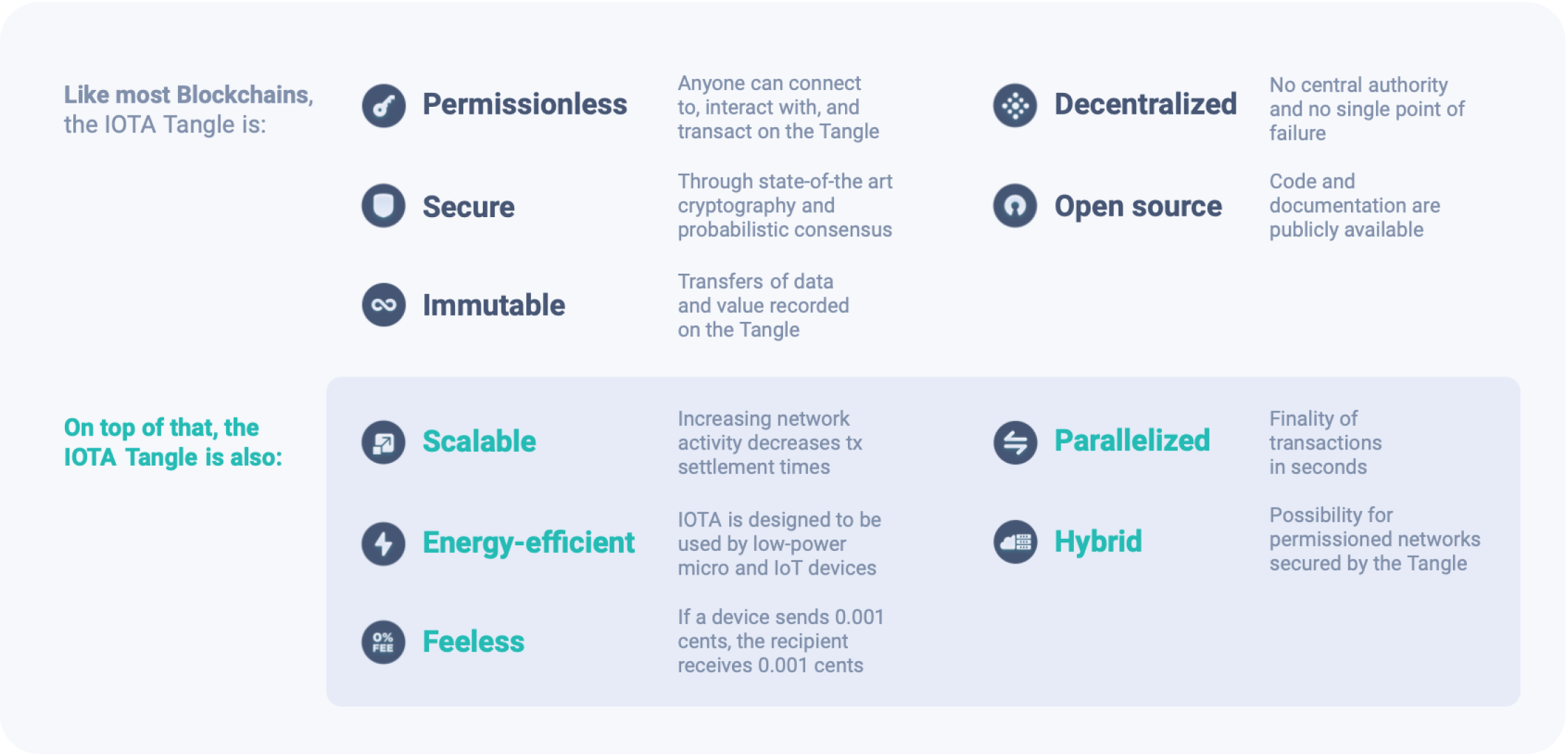
Don’t worry, all of this is happening under the hood. This means that the more an individual utilizes the network (sending transactions to the Tangle) the more he or she is also contributing to the infrastructure by confirming previous transactions. Due to this structure, the IOTA network is a cooperative network, whereas traditional blockchain networks usually utilize a competitive structure where transactions “fight” with high fees for one of the limited slots in a block: the higher your fee, the more likely it is to be included.
The Tangle does not take a fee for transactions. This is important because it enables not only feeless data transactions but also feeless IOTA Token transactions which can be as low as a fraction of a cent and thus suitable for micropayments, whereas in most other DLTs or blockchains the fee is already higher than the micropayment.
Last but not least: the Tangle is designed to be “green” and to have maximum efficiency in terms of its energy requirements. The energy usage of just one Bitcoin transaction can power between 600 Million and 1 Billion IOTA transactions.
Frameworks

On top of the Tangle, the IOTA Foundation is developing frameworks that extend the core protocol using freely available building blocks that anyone can tailor to their needs, to enable a wide range of functionalities for DLT use cases:
- Digital Identity: IOTA Identity establishes trust and interoperability across organizations, individuals and devices, and enables the development of identity solutions in a production-ready, open-source environment. It is the only decentralized identity solution that runs on the mainnet of a feeless, permissionless DLT. Please also check out the IOTA Digital Identity presentation.
- Tokenized Assets: Tokenization allows real-world assets to be managed, traded, bought, and sold on a DLT. There are more use cases for tokenized assets than can be comprehensively described in this article, but one important use case is the creation of NFTs (Non-fungible tokens) to replicate ownerships of digital and physical assets securely in the digital realm.
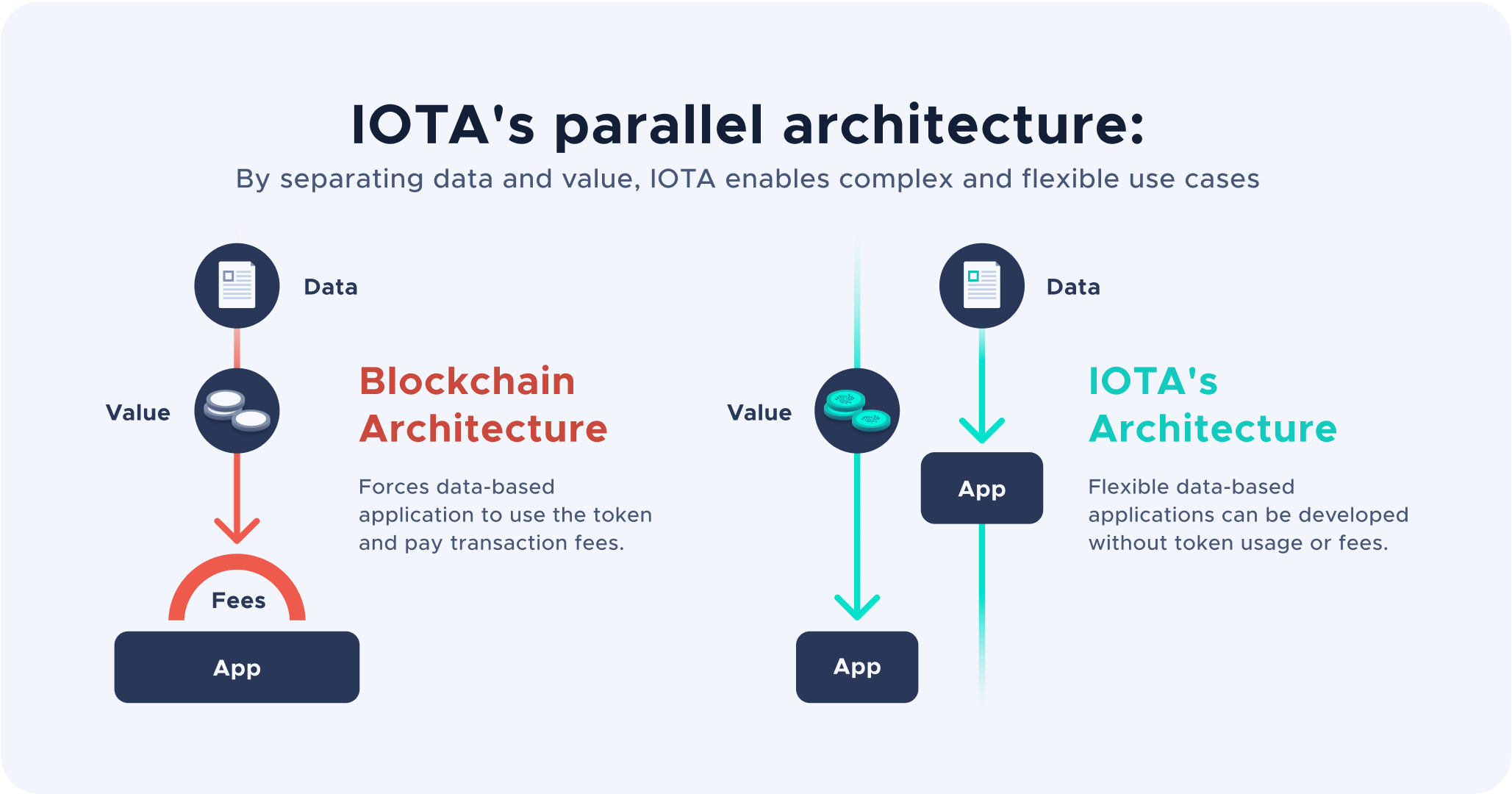
- Streams: IOTA Streams is an organizational tool for structuring and navigating secure data through the Tangle. Streams organizes data by ordering it in a uniform and interoperable structure. Whereas single transactions are “spread” over a DLT, Streams formats those transactions into a secure virtual data channel.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts leave an immutable audit trail on the distributed ledger and their automation saves time and money for the parties involved. The concept is simple and can be applied to just about every industry in a variety of use cases, from tracking goods throughout the supply chain to exchanging ownership of stocks and bonds.
- Access: IOTA Access is an open-source framework used to build access control systems for smart devices. It is designed to work with any IoT resource, whether it is a vehicle, smart lock or embedded sensor.
- IOTA Stronghold: Stronghold is a secure software implementation with the sole purpose of protecting digital secrets from exposure to hackers and accidental leaks. Stronghold is already integrated within the Firefly Wallet (IOTA Token Management) to provide an effective way to securely store and handle the private keys of the user without a hardware wallet. In the near future, we plan to add Stronghold to IOTA Streams as well as IOTA Identity.
The above frameworks provide developer interfaces (SDKs) to interact with.
The last technical element is the Firefly wallet, the secure entry point for users to the IOTA ecosystem. Firefly is built with the future in mind and uses cutting-edge Stronghold technology, to not have to worry too much about security. With its modular design, Firefly enables future functionalities like voting with your token ownership on decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) decisions. Firefly also replaces the deprecated Light wallet and Trinity wallet.
All of the above components make up the technical part of IOTA. The entry point for more information and technical documentation is the new IOTA Wiki. We encourage you to contribute to the IOTA Wiki and share your IOTA know-how with the world to inform your fellow IOTA community peers and jointly create a one-stop shop for organizations to learn about IOTA.
Let’s take a look at the non-technical parts

IOTA is built with the long-term vision of enabling the machine economy and connecting billions of persons, organizations and devices. Therefore, requirements are a key part to drive innovation, research and development. One effect of an increasingly connected world is the new regulations to which businesses must adapt. In order to not only fulfill these requirements but also to enable new models, we provide the above-mentioned IOTA frameworks for implementation. In the future, we aim to build additional functionalities that further abstract the existing framework functionalities – for example, track and trace functionalities to enable a simpler onboarding of developers in those industries.
For the same reason, we always aim for compatibility with existing standards, for example following the W3C for the IOTA Identity implementation. Together with the Eclipse Foundation, we have launched TangleEE (Tangle Enterprise Edition) to provide external governance and aggregate corporate developers around IOTA. We are currently validating the next steps with the involved organizations to provide the best benefit for all stakeholders.

In parallel, the IOTA Foundation is working closely with OMG (the Object Management Group) to standardize the workings of the Tangle as well as the node software. This means that IOTA not only exists as software but that all interactions, formats and specifications are formally documented, which enables organizations to write their own implementation.

As part of IOTA’s vision of providing a free open source infrastructure for new business models, we engage and work closely with different entities to understand their requirements, solve specific industry problems and offer a broad range of functionalities to users of IOTA across a range of industry verticals, such as mobility and automotive, global trade or supply chain. Our in-house domain expertise in these and other areas enables constructive dialogue and joint implementation of IOTA into the technology stack of partner organizations.
Moving up one layer, the commercial entities are not only governed by regulations but also engage with public institutions and cities to improve our public services. This includes protecting the privacy of individuals, decarbonizing industries through near-real-time emissions monitoring, reporting and verification, improving traffic management, or increasing the traceability of goods.

The IOTA Foundation works closely with regulatory bodies and public sector representatives to understand the impact of DLT and shape technical and regulatory standards and frameworks. The IOTA Foundation is a founding member of INATBA (the International Association for Trusted Blockchain Applications) and collaborates with public sector representatives on the opportunities, barriers and shortcomings of DLT and blockchain through various working groups.

At the top of the ecosystem infographic, only one actor is left: Society. You, the reader, elect public sector representatives, based on your own requirements and ambitions, such as access to cleaner water, better data protection, or managing previously paper-based errands through new secure and digital environments – for example, directly from the device you are reading this on.
For more information please visit the following links:
- IOTA Business Ecosystem Infographic
- IOTA Wiki
- IOTA Short Pitch presentation
- Useful IOTA online Resources (Presentations, Whitepapers, etc.)
- How IOTA works - Introduction
The Road to Integration Series:




